La sécurité est un objet de recherche protéiforme et mouvant par excellence, pour preuve l’incontournable entrée en matière l’évoquant en général comme un concept essentiellement contesté. Ainsi, aborder la question de l’ action de l’État en matière de sécurité renvoie à des univers sociaux et des pratiques extrêmement diverses. En mobilisant le concept de champ, ce chapitre propose de penser de manière relationnelle la production des savoirs sur l’(in)sécurité comme émanant d’un espace social autonome et dynamique généré par des agents pouvant être définis comme des professionnels de la gestion de la menace et des inquiétudes. Issue d’un projet de recherche financé par le Fonds national suisse de la recherche scientifique, la contribution a le double objectif de mobiliser la littérature existante sur le champ de la sécurité afin d’analyser les dynamiques contemporaines de sécurité en Suisse et de proposer des solutions pratiques pour tout chercheur souhaitant mener une analyse systématique de la sorte.
La sécurité est un objet de recherche protéiforme et mouvant par excellence, pour preuve l’incontournable entrée en matière l’évoquant en général comme un concept essentiellement contesté. Ainsi, aborder la question de l’ action de l’État en matière de sécurité renvoie à des univers sociaux et des pratiques extrêmement diverses. En mobilisant le concept de champ, ce chapitre propose de penser de manière relationnelle la production des savoirs sur l’(in)sécurité comme émanant d’un espace social autonome et dynamique généré par des agents pouvant être définis comme des professionnels de la gestion de la menace et des inquiétudes. Issue d’un projet de recherche financé par le Fonds national suisse de la recherche scientifique, la contribution a le double objectif de mobiliser la littérature existante sur le champ de la sécurité afin d’analyser les dynamiques contemporaines de sécurité en Suisse et de proposer des solutions pratiques pour tout chercheur souhaitant mener une analyse systématique de la sorte.
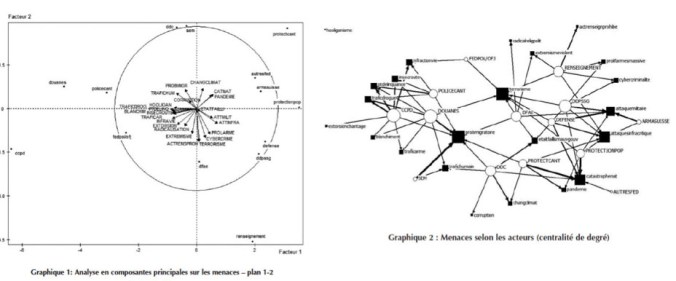
Graphique 1 : Menaces selon les acteurs (centralité de degré)
Davidshofer, Stephan; Tawfik, Amal; Hagmann, Jonas (2023). La politique de sécurité comme produit du rapport de forces au sein du champ. Le cas de la Suisse au milieu des années 2010. In: Dubois, Vincent (ed.). Les structures sociales de l’action publique : Analyser les politiques publiques avec la sociologie des champs, pp127-163. Paris: Editions du Croquant. PDF
 It is widely known that national security fields changed considerably in the last decades. Different from the late Cold War years, when they focused on military threats, were closely orchestrated by Defence Ministries and contained few international contacts, national security ‘systems’ today handle wide sets of dangers, draw on complex casts of actors across levels of government, and often maintain working relations with multiple foreign partners. This comprehensive reconfiguration of national security fields is a central theme to security scholars and policymakers alike – but also difficult to pin down for methodological reasons. Written documentation on security agencies does not give precise indication of actual everyday inter-agency work practices, and assessments of nationwide security work across functions and levels of government are challenging by sheer questions of size. Adopting a practice-oriented approach to security research, this article draws on an unparalleled nationwide data collection effort to differentiate and map-out the Swiss security field’s programmatic and institutional evolution.
It is widely known that national security fields changed considerably in the last decades. Different from the late Cold War years, when they focused on military threats, were closely orchestrated by Defence Ministries and contained few international contacts, national security ‘systems’ today handle wide sets of dangers, draw on complex casts of actors across levels of government, and often maintain working relations with multiple foreign partners. This comprehensive reconfiguration of national security fields is a central theme to security scholars and policymakers alike – but also difficult to pin down for methodological reasons. Written documentation on security agencies does not give precise indication of actual everyday inter-agency work practices, and assessments of nationwide security work across functions and levels of government are challenging by sheer questions of size. Adopting a practice-oriented approach to security research, this article draws on an unparalleled nationwide data collection effort to differentiate and map-out the Swiss security field’s programmatic and institutional evolution.

 How do notions of collective international insecurity come about, and what are their effects on foreign policy-making? The Copenhagen School’s securitization theory offers a powerful take on the political construction of threats. In its original variant, however, the theory focuses strongly on the deontic (norm-breaking) powers of ‘security talk’ – and not on the threat sceneries that the latter substantively describes. This article addresses this latter link by reworking securitization into a positional/relational argument. Seen its way, the framing of something as threatening comes with larger – often implicit – claims about threatening and threatened actors in world politics. The empirical cases on post-war France and West Germany show how securitization equals an epistemological systematization of international affairs, for the political construction of collective international danger becomes an ordering process that conditions foreign policy strategizing.
How do notions of collective international insecurity come about, and what are their effects on foreign policy-making? The Copenhagen School’s securitization theory offers a powerful take on the political construction of threats. In its original variant, however, the theory focuses strongly on the deontic (norm-breaking) powers of ‘security talk’ – and not on the threat sceneries that the latter substantively describes. This article addresses this latter link by reworking securitization into a positional/relational argument. Seen its way, the framing of something as threatening comes with larger – often implicit – claims about threatening and threatened actors in world politics. The empirical cases on post-war France and West Germany show how securitization equals an epistemological systematization of international affairs, for the political construction of collective international danger becomes an ordering process that conditions foreign policy strategizing.