What is a city and how do we recognize and assess security dispositives in public spaces? This chapter draws on my research program and fieldwork in Switzerland, Morocco, Nepal and Uruguay. It presents ways of systematizing urban space, and discusses how research on human, digital, physical and conceptual urban control elements can be operationalized: How can we create case studies representative of an entire city? What role do interviews play and whom should we talk to to collect data? Can we retrace practices across longer periods of time? And then – how to compare findings across radically different cities/polities? Urban security practices are extraordinarily rich, deterritorialised and interdisciplinary. A critical approach to data collection and analysis allows recognizing this – and it helps to avoid reproducing simplistic and universalizing accounts of security.
Taxi-time in Montevideo: Sub-city labs, simplified research itinerary
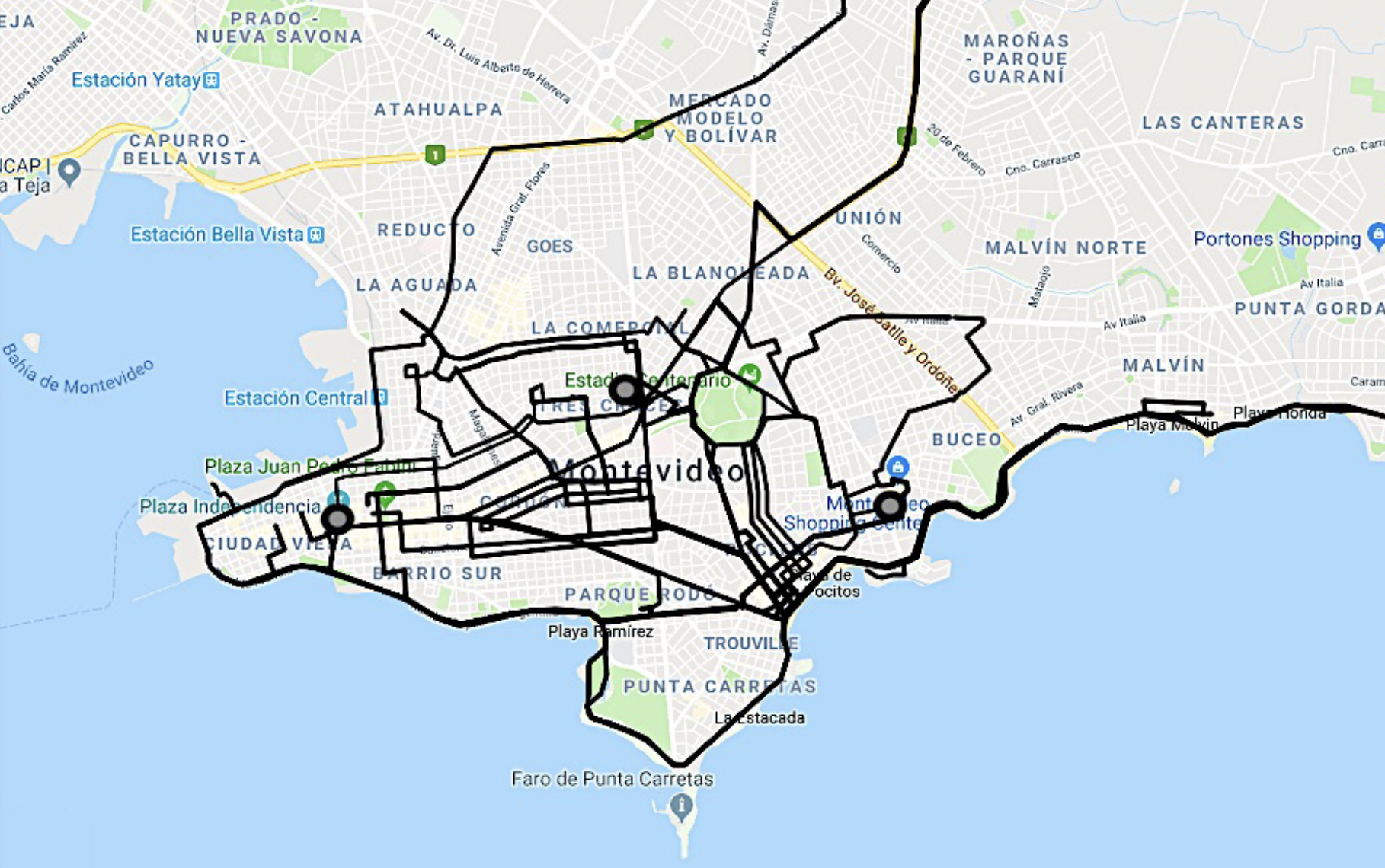
Hagmann, Jonas (2023). Mapping urban security practices. In: Salter, Mark; Mutlu, Can; Frowd, Philippe (eds.). Research Methods in Critical Security Studies, pp145-154. London: Routledge. PDF













 La sécurité est un objet de recherche protéiforme et mouvant par excellence, pour preuve l’incontournable entrée en matière l’évoquant en général comme un concept essentiellement contesté. Ainsi, aborder la question de l’ action de l’État en matière de sécurité renvoie à des univers sociaux et des pratiques extrêmement diverses. En mobilisant le concept de champ, ce chapitre propose de penser de manière relationnelle la production des savoirs sur l’(in)sécurité comme émanant d’un espace social autonome et dynamique généré par des agents pouvant être définis comme des professionnels de la gestion de la menace et des inquiétudes. Issue d’un projet de recherche financé par le Fonds national suisse de la recherche scientifique, la contribution a le double objectif de mobiliser la littérature existante sur le champ de la sécurité afin d’analyser les dynamiques contemporaines de sécurité en Suisse et de proposer des solutions pratiques pour tout chercheur souhaitant mener une analyse systématique de la sorte.
La sécurité est un objet de recherche protéiforme et mouvant par excellence, pour preuve l’incontournable entrée en matière l’évoquant en général comme un concept essentiellement contesté. Ainsi, aborder la question de l’ action de l’État en matière de sécurité renvoie à des univers sociaux et des pratiques extrêmement diverses. En mobilisant le concept de champ, ce chapitre propose de penser de manière relationnelle la production des savoirs sur l’(in)sécurité comme émanant d’un espace social autonome et dynamique généré par des agents pouvant être définis comme des professionnels de la gestion de la menace et des inquiétudes. Issue d’un projet de recherche financé par le Fonds national suisse de la recherche scientifique, la contribution a le double objectif de mobiliser la littérature existante sur le champ de la sécurité afin d’analyser les dynamiques contemporaines de sécurité en Suisse et de proposer des solutions pratiques pour tout chercheur souhaitant mener une analyse systématique de la sorte.
 In 1975–1976, Lebanon and the city of Beirut were consumed by devastating armed conflict. But whereas this empirical fact is uncontested, its historical causes and political meanings remain controversial. Sara Fregonese’s book War and the Cityfocuses on the rationalisation of the conflict and asks: Do Western descriptions of the war live up to the realities observed in Beirut? War and the City puts the spotlight on important political practices, which are the ways actors co-construct meaning in and through their own urban environments, and how those interpretations may develop differently from far-away truth claims. This said, the book also includes (exceedingly) structuralist narratives, and it raises important questions about whose perspectives (in Beirut) are listened to and heard. Furthermore, its treatments of works from related disciplines – security studies and International Relations especially – is underdeveloped if not outright crude.
In 1975–1976, Lebanon and the city of Beirut were consumed by devastating armed conflict. But whereas this empirical fact is uncontested, its historical causes and political meanings remain controversial. Sara Fregonese’s book War and the Cityfocuses on the rationalisation of the conflict and asks: Do Western descriptions of the war live up to the realities observed in Beirut? War and the City puts the spotlight on important political practices, which are the ways actors co-construct meaning in and through their own urban environments, and how those interpretations may develop differently from far-away truth claims. This said, the book also includes (exceedingly) structuralist narratives, and it raises important questions about whose perspectives (in Beirut) are listened to and heard. Furthermore, its treatments of works from related disciplines – security studies and International Relations especially – is underdeveloped if not outright crude. How do urban security assemblages evolve? Scholars inspired by Deleuze’s influential Control Thesis see profound shifts in the ways urban security operates. Different to Foucault’s disciplinary logics, they argue, urban security assemblages now rely intimately on expanding casts of policing agents, digital surveillance and statistical knowledge(s). They reach beyond enclosures and national borders, and they challenge democratic politics ever more forcefully. Whether this general trajectory of security management holds true across the global cityscape is yet far from evident. Not only do most studies of contemporary control draw conclusions from European and North American cities exclusively. Many also reproduce and project abroad distinctively Eurocentric assumptions about state-society relations, governance and insecurity. This upcoming new article in Journal of Global Security Studies first foregrounds and problematizes these penchants. It then looks at the Moroccan city of Marrakech to detail how urban security assemblages may evolve in different ways, at other speeds, and following different steering logics than what is generally set out by research on control. The article concludes with a discussion of how insights offered by places such as Marrakech contribute to more robust, analytically refined and globally inclusive research on the contemporary politics of urban security.
How do urban security assemblages evolve? Scholars inspired by Deleuze’s influential Control Thesis see profound shifts in the ways urban security operates. Different to Foucault’s disciplinary logics, they argue, urban security assemblages now rely intimately on expanding casts of policing agents, digital surveillance and statistical knowledge(s). They reach beyond enclosures and national borders, and they challenge democratic politics ever more forcefully. Whether this general trajectory of security management holds true across the global cityscape is yet far from evident. Not only do most studies of contemporary control draw conclusions from European and North American cities exclusively. Many also reproduce and project abroad distinctively Eurocentric assumptions about state-society relations, governance and insecurity. This upcoming new article in Journal of Global Security Studies first foregrounds and problematizes these penchants. It then looks at the Moroccan city of Marrakech to detail how urban security assemblages may evolve in different ways, at other speeds, and following different steering logics than what is generally set out by research on control. The article concludes with a discussion of how insights offered by places such as Marrakech contribute to more robust, analytically refined and globally inclusive research on the contemporary politics of urban security.

 Urban design is increasingly widely used for city-oriented security production, and thus becomes included into the latter’s complex politics of in- and exclusion. This contribution showcases how urban design becomes deployed as a technology of security both internationally and in Switzerland, and how a reflexive security studies perspective on this use offers productive new research avenues. This is because the focus on urban design allows asking in new ways whether ‘more security is better’, how technological interventions are used and appropriated, and how they reconfigure democratic processes. Security research drawing on reflexive IR and security studies is well placed to this endeavour, as it proposes integrative and dialectical analyses of how built environments may be empowering/disempowering and inclusive/exclusive. The contribution sets out the specificities of this research ontology, presents urban design’s operation as technology of security politics, and illustrates said link in two mini-case studies centring in Bogotá and Zürich. In line with the special section to which it contributes, the article seeks to familiarize readers with architecture-oriented political analysis, and to draw out main lines of further investigation.
Urban design is increasingly widely used for city-oriented security production, and thus becomes included into the latter’s complex politics of in- and exclusion. This contribution showcases how urban design becomes deployed as a technology of security both internationally and in Switzerland, and how a reflexive security studies perspective on this use offers productive new research avenues. This is because the focus on urban design allows asking in new ways whether ‘more security is better’, how technological interventions are used and appropriated, and how they reconfigure democratic processes. Security research drawing on reflexive IR and security studies is well placed to this endeavour, as it proposes integrative and dialectical analyses of how built environments may be empowering/disempowering and inclusive/exclusive. The contribution sets out the specificities of this research ontology, presents urban design’s operation as technology of security politics, and illustrates said link in two mini-case studies centring in Bogotá and Zürich. In line with the special section to which it contributes, the article seeks to familiarize readers with architecture-oriented political analysis, and to draw out main lines of further investigation.


 It is generally accepted today that major international events – such as in 1914, 1945, 1989 or 2001 – contribute to guiding IR scholarship’s interests. But it remains poorly explored how, beyond substantive focus, transformative political events affect the academic field’s own working and organization. Whereas we know that global key moments (such as the end of the Cold War) were or are experienced differently by different societies, at the policy level, in terms of identity-construction and historiography, it remains to explore how such changes influence scholarly work in different higher education systems. Our article in International Studies Perspectives focuses on this link. It centers on the role of institutional factors in the conditioning of IR scholarship, which it sees as important yet under-explored intervening elements in the interrelation between political events and academic practice. The article defines the utility of such focus and illustrates it with casework centering on the end of the Cold War, and three central parties to the Cold War conflict – Russia as representative of the Eastern Bloc, Canada of the Western Alliance, and Switzerland as a Neutral polity. In doing so, the article showcases how institutional factors such as funding schemes, the marketization of education or creation of new IR departments operate as effective ‘hinges’, exerting significant influence over the ways scholars develop ideas about international relations.
It is generally accepted today that major international events – such as in 1914, 1945, 1989 or 2001 – contribute to guiding IR scholarship’s interests. But it remains poorly explored how, beyond substantive focus, transformative political events affect the academic field’s own working and organization. Whereas we know that global key moments (such as the end of the Cold War) were or are experienced differently by different societies, at the policy level, in terms of identity-construction and historiography, it remains to explore how such changes influence scholarly work in different higher education systems. Our article in International Studies Perspectives focuses on this link. It centers on the role of institutional factors in the conditioning of IR scholarship, which it sees as important yet under-explored intervening elements in the interrelation between political events and academic practice. The article defines the utility of such focus and illustrates it with casework centering on the end of the Cold War, and three central parties to the Cold War conflict – Russia as representative of the Eastern Bloc, Canada of the Western Alliance, and Switzerland as a Neutral polity. In doing so, the article showcases how institutional factors such as funding schemes, the marketization of education or creation of new IR departments operate as effective ‘hinges’, exerting significant influence over the ways scholars develop ideas about international relations.
 Contemporary security practices rarely represent new inventions – albeit change is important to it, the security politics of today often has a very long lineage. It adapts, reworks and sometimes just rehashes old ideas and practices of policing, and is embedded in deeply entrenched, historically grown and power-laden frameworks of collective, national, local or international sense- and decision-making. This contribution to Contemporanea‘s Special Section on the “History of Transnational Security Management in Europe” argues that is
Contemporary security practices rarely represent new inventions – albeit change is important to it, the security politics of today often has a very long lineage. It adapts, reworks and sometimes just rehashes old ideas and practices of policing, and is embedded in deeply entrenched, historically grown and power-laden frameworks of collective, national, local or international sense- and decision-making. This contribution to Contemporanea‘s Special Section on the “History of Transnational Security Management in Europe” argues that is